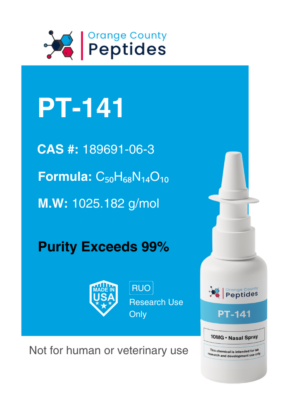
MGF – 5mg
$50.00
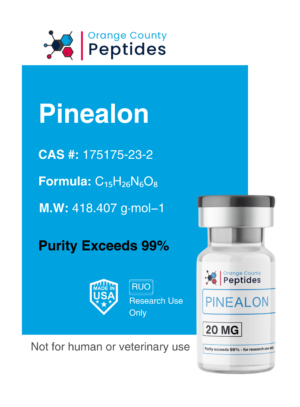
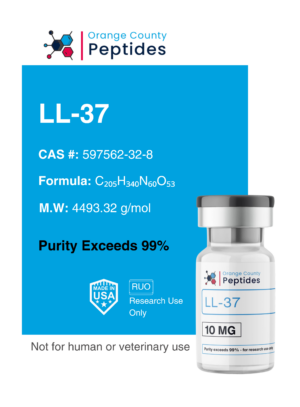
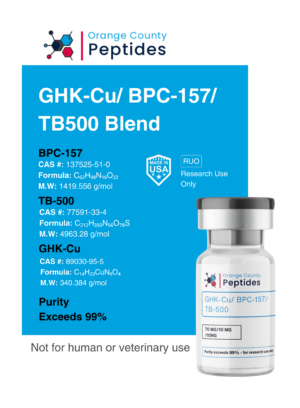
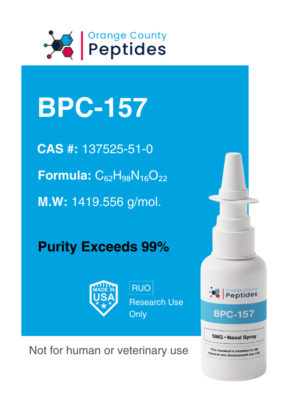
MGF (Mechano Growth Factor)
MGF is a splice variant of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) involved in muscle repair and regeneration. It is studied for its potential to promote muscle recovery, repair damaged tissues, and enhance overall muscle function. Researchers are particularly interested in its applications for muscle recovery, tissue repair, and benefits in addressing muscle-wasting conditions.
Potential Research Applications
MGF is being explored in research settings for its role in:
- Muscle Regeneration & Repair: Investigated for its ability to stimulate muscle cell growth and aid in recovery following stress or injury.
- Muscle Growth: Studied for its role in enhancing muscle hypertrophy and increasing muscle mass in response to exercise or mechanical stress.
- Tissue Repair & Recovery: Researched for its potential to accelerate the repair of damaged tissues, making it relevant in sports and regenerative medicine.
- Age-Related Muscle Loss: Explored for its potential to combat muscle wasting and sarcopenia in aging populations or individuals with degenerative muscle conditions.
✔ High-Quality Research Peptide – Produced under stringent quality control standards.
✔ Lab-Tested for Purity – Ensures consistency for scientific studies.
✔ Research Use Only – Not for human consumption or medical applications.
✔ Peptides – Will arrive in a lyophilized (powder) form for maximum stability.
- Description
- Certificate of Analysis
MGF, a splice variant of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1), plays a key role in muscle repair, regeneration, and growth. The body produces MGF in response to mechanical stress or muscle injury, making it essential for recovery. Researchers study MGF for its potential applications in muscle healing, tissue regeneration, and performance enhancement. Because MGF influences muscle adaptation, it has gained attention in sports medicine, rehabilitation, and aging research.
The body releases MGF following physical activity or muscle damage, especially after resistance training or injury. MGF activates satellite cells, which are specialized muscle stem cells critical for muscle repair and regeneration. These cells multiply and fuse with existing muscle fibers, repairing damaged tissue and promoting muscle growth. In addition, MGF boosts protein synthesis and regulates other growth factors, making it valuable for recovery after intense exercise or injury.
Unlike other IGF-1 variants, MGF has a unique structure with a distinct C-terminal extension. This structure gives MGF localized action within muscle tissue, setting it apart from IGF-1’s broader systemic effects. Researchers focus on MGF’s role in muscle-wasting disorders, faster recovery times, and improving muscle function after physical activity. Because muscle degeneration is a concern in aging and disease, scientists are exploring how MGF may help preserve muscle mass and strength.
MGF is a key focus in research on sports performance, rehabilitation, and aging-related muscle loss. It may help regenerate muscle tissue and speed up recovery, especially in cases of sarcopenia, severe muscle injuries, or post-surgical healing. Some studies suggest MGF could improve athletic performance by accelerating muscle repair and growth. By increasing muscle adaptation, MGF may offer benefits for individuals recovering from injuries or looking to maintain muscle function as they age.
Additionally, researchers explore whether MGF could support nerve regeneration and recovery from neuromuscular injuries. Since muscle health is closely linked to nervous system function, MGF’s potential benefits may extend beyond muscle repair alone. Scientists continue investigating whether MGF can aid in neurological recovery and conditions involving muscle atrophy due to nerve damage.
Although MGF shows promise, ongoing studies aim to fully understand its effects, long-term safety, and therapeutic potential. Researchers continue to evaluate MGF in controlled settings to determine its full range of applications. Because MGF plays a role in muscle adaptation, it remains a major subject of interest in regenerative medicine and sports science.
For Research Use Only.
No Certificate of Analysis images available for this product.
Frequently bought together