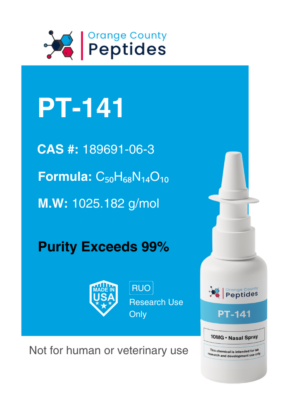
Oxytocin – 10mg
$50.00
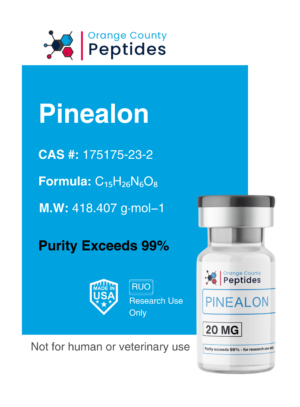
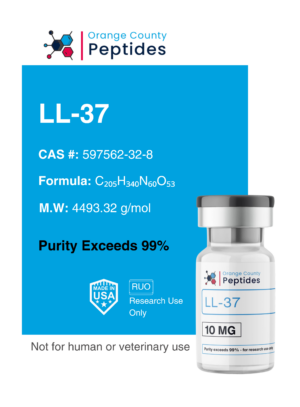
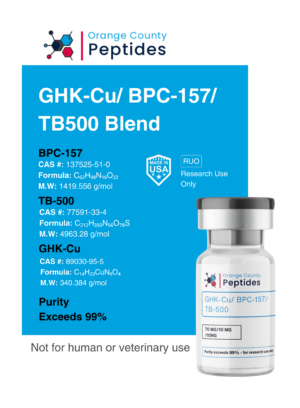
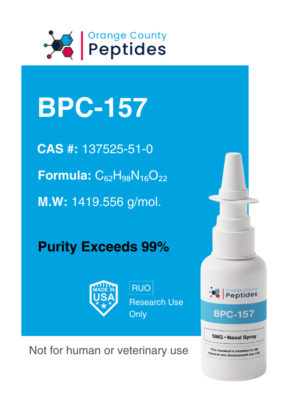
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neurotransmitter known for its role in childbirth, lactation, and social bonding. Often called the “love hormone,” it promotes emotional connections, trust, and positive social interactions. In addition to its role in reproduction, Oxytocin is being studied for its potential therapeutic applications in mental health, including anxiety, depression, and autism spectrum disorders. Researchers are also exploring its influence on muscle recovery and mood regulation through its effects on the central nervous system.
Potential Research Applications
Oxytocin is currently being studied for its role in:
- Social Bonding & Emotional Regulation: Investigated for its effects on empathy, trust, and social connections, with potential benefits in mental health and interpersonal relationships.
- Mental Health & Stress Reduction: Researched for its ability to alleviate anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders by modulating stress responses and promoting relaxation.
- Childbirth & Lactation: Studied for its role in stimulating uterine contractions and promoting milk ejection during breastfeeding.
- Cognitive & Behavioral Health: Explored for its potential benefits in conditions like autism spectrum disorders, social anxiety, and other behavioral issues.
- Muscle Recovery & Healing: Investigated for its ability to support tissue repair and recovery after physical exertion or injury.
✔ High-Quality Research Peptide – Produced under stringent quality control standards.
✔ Lab-Tested for Purity – Ensures consistency for scientific studies.
✔ Research Use Only – Not for human consumption or medical applications.
✔ Peptides – Will arrive in a lyophilized (powder) form for maximum stability.
- Description
- Certificate of Analysis
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide that plays a vital role in childbirth, lactation, and social bonding. The hypothalamus produces oxytocin, and the posterior pituitary gland releases it into the bloodstream. It stimulates uterine contractions during labor and helps trigger milk release during breastfeeding. Often referred to as the "love hormone," oxytocin fosters emotional bonding and strengthens social connections.
During labor, oxytocin signals the uterus to contract, aiding in childbirth. After delivery, it continues to support maternal health by triggering milk ejection from the mammary glands, ensuring successful breastfeeding. These functions make oxytocin essential for reproductive health and maternal care. Because of its crucial role in labor and postpartum recovery, synthetic oxytocin is sometimes administered to induce labor or manage bleeding after childbirth.
Beyond its reproductive functions, oxytocin influences emotions, trust, and social interactions. Studies show that oxytocin enhances bonding between parents and children, deepens emotional connections in romantic relationships, and promotes empathy in social interactions. Levels of oxytocin naturally rise during physical affection, such as hugging, touching, or engaging in positive social experiences.
In addition to its effects on bonding, oxytocin is being studied for its impact on mental and physical health. Research suggests that oxytocin may help reduce anxiety, depression, and stress. Because of this, scientists are exploring its potential use in treating social anxiety disorder, autism spectrum disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The ability of oxytocin to regulate emotional responses makes it a promising subject in neuroscience and psychology.
Oxytocin may also play a role in pain perception. Studies indicate that it has analgesic effects, reducing pain sensitivity during childbirth and post-surgical recovery. Some research suggests that oxytocin could help with chronic pain conditions by interacting with pain-processing pathways in the nervous system. This has led scientists to explore its potential for non-opioid pain management.
Besides its influence on mood and pain, oxytocin may also affect cardiovascular health. Some studies indicate that oxytocin helps lower blood pressure and reduce stress-related inflammation, which could have protective effects on heart health. Although research in this area is still ongoing, it highlights the diverse functions of oxytocin beyond social bonding and reproduction.
Despite its many potential benefits, further studies are needed to fully understand oxytocin’s mechanisms, appropriate dosages, and long-term safety. Synthetic oxytocin is available for medical use, but its effects outside controlled environments require further investigation. Unregulated or excessive use may carry risks, reinforcing the need for responsible research and medical supervision.
Overall, oxytocin remains a major focus of scientific research due to its essential role in reproductive health, emotional bonding, mental well-being, and pain regulation. As studies continue to uncover new applications, oxytocin may offer innovative treatments for social, psychological, and medical conditions.
For Research Use Only.
No Certificate of Analysis images available for this product.
Frequently bought together