P21 – 10mg
$50.00
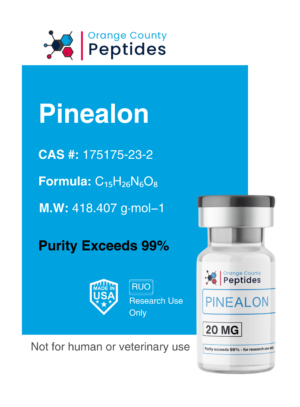
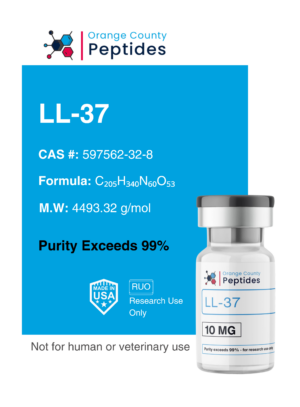
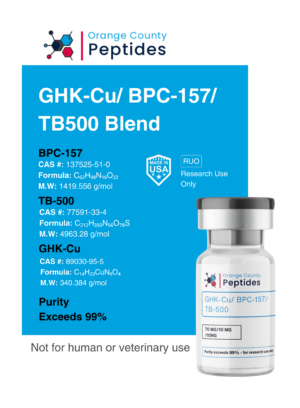
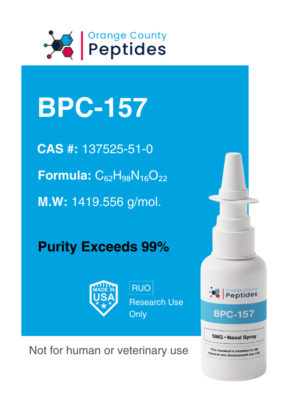
P21
P21, also called CDKN1A, is a protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). It is essential for controlling cell growth, division, and survival. Researchers have also explored its role in aging, tissue regeneration, and cellular stress responses.
Potential Research Applications
P21 is currently being investigated for its role in:
- Cell Cycle Regulation & Cancer Research: Explored for its ability to control cell cycle progression, making it crucial in preventing cancer cell proliferation.
- Aging & Cellular Senescence: Researched for its involvement in cellular senescence, a process that influences aging and age-related diseases.
- Tissue Regeneration & Repair: Studied for its role in modulating tissue regeneration, especially during cellular stress and injury recovery.
- DNA Damage Response & Repair: Investigated for its role in DNA repair mechanisms following damage from oxidative stress or radiation.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Explored for its potential impact on cellular processes linked to neurodegeneration, with applications in conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease.
✔ High-Quality Research Peptide – Produced under stringent quality control standards.
✔ Lab-Tested for Purity – Ensures consistency for scientific studies.
✔ Research Use Only – Not for human consumption or medical applications.
✔ Peptides – Will arrive in a lyophilized (powder) form for maximum stability.
- Description
- Certificate of Analysis
P21 is a protein encoded by the CDKN1A gene that helps regulate the cell cycle and control phase progression. As a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, P21 blocks cyclin-CDK2 and cyclin-CDK4 complexes, which are essential for moving from the G1 phase to the S phase. By stopping these complexes, P21 prevents uncontrolled cell growth and supports tumor suppression.
When cells experience DNA damage or stress—such as oxidative stress, UV radiation, or oncogene activation—they increase P21 production. This protein plays a central role in the p53 signaling pathway, which controls cell cycle arrest and programmed cell death (apoptosis). When a cell detects DNA damage, p53 activates P21, stopping the cell cycle to allow repairs. If the damage is too severe, P21 helps trigger apoptosis to remove the damaged cell.
Beyond controlling cell division, P21 plays a role in apoptosis, cell specialization, and aging. Scientists have linked it to cancer, degenerative diseases, and other conditions related to cell stability. By maintaining genetic stability, P21 helps prevent mutations that could lead to tumor growth. However, in some cases, high levels of P21 may promote tumor resistance to treatment, making its role complex in cancer research.
Researchers often use P21 as a marker to study how cells respond to stress and DNA damage. They also explore whether modifying P21 levels could be useful in cancer therapy. Since P21 can either slow or promote tumor growth depending on the context, scientists continue to investigate its potential benefits and risks.
Some studies suggest that P21 also influences aging by promoting cellular aging (senescence) and limiting excessive cell growth. Because of this, researchers are exploring whether P21 plays a role in age-related diseases. Understanding how P21 interacts with different biological pathways could help develop new treatments for cancer, aging, and other conditions.
Although P21 has been widely studied, researchers are still uncovering its full effects and therapeutic potential. Since its impact varies depending on the tissue and disease, further studies are needed to determine how to use P21 for medical applications.
For Research Use Only.
No Certificate of Analysis images available for this product.
Frequently bought together